Usually, whenever I boil eggs, I set the induction power to 600 W and wait for 30 minutes. During this time, I sometimes felt that the egg yolk was a little overcooked. I always had a doubt whether I was supplying more energy than needed, or if the energy supplied for 30 minutes was optimal. I was curious to know the optimal time required to boil the eggs perfectly at 600 W induction power settings. So, I went back to the basics of thermodynamics to find the optimal time to boil the eggs perfectly.
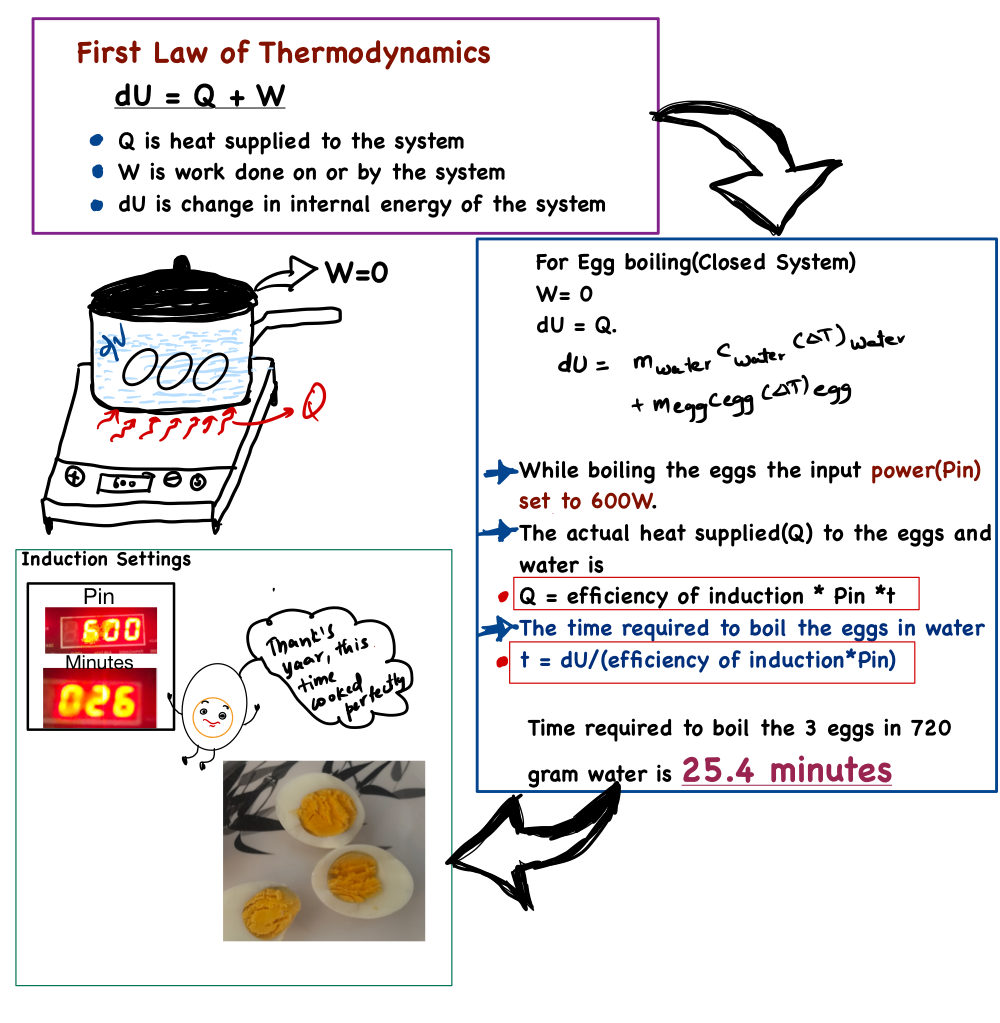
So, if we dive into thermodynamics, the First law of the thermodynamics tells us that the change in the internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system plus the work done on or by the system
$$\Delta U = Q + W$$
where,
- $\Delta U$ is internal energy of the system
- Q is heat supplied to the system
- W work done by or on the system.
If work done by the system, W is negative.
If work done on the system, W is positive.
Since I closed the container with a lid, I assumed it to be a closed system. Overall energy losses of the closed system were accounted for while evaluating the efficiency of the induction.
What is closed loop system and what are the other system types in thermodynamics
- Open System: Transfer mass and energy to the surroundings.
- Closed System: No mass transfer only energy transfer to the surroundings.
- Isolated system: No mass and energy transfer to the surroundings.
In the case of boiling eggs, there is no work is done on or by the system. Therefore, W=0, hence, the heat supplied by the induction cooker is used entirely to change the internal energy of the water and the eggs.
$$Q=\Delta U$$
where,
- $\Delta U=mc\Delta T$
- $m$ mass of the system
- $c$ is specific heat of the system
- $\Delta T$ is Difference between initial and final temperature
Referring to above formula, the heat required to boil the eggs in water is
$$\Delta U = \Delta U_{egg} + \Delta U_{water}$$
$$\Delta U = m_{water}c_{water}(\Delta T)_{water} + m_{egg}c_{egg}(\Delta T)_{egg}$$
In the process, the first step is to determine how much heat is actually used (i.e., the efficiency) when the induction stove is set to 600W.
The efficiency can be calculated using below formula.
$$ \eta= \frac{Q}{Q_{induction}}$$
To find the efficiency, I took a fixed amount of water and measured its initial and final temperatures using the food thermometer over a fixed time period. I then calculated the heat required($Q$) and the heat supplied($Q_{Induction}$) using the following formulas.
$$Q = m_{water}c_{water}(\Delta T)_{water}$$
$$Q_{\text{induction}} = P_{\text{in}} \times t$$
Four trials were conducted to estimate the efficiency of the induction stove, and the results are shown in the table below.
| With LID | Initial Temp(degree) | Final Temp(degree) | C ( kJ/kg·°C) | mass (kg) | $Q$ (KJ) | Minutes (t) | Seconds (t) | Power in (Pin) (W) | Total Energy Supplied $Q_{Induction}$ (KJ) | Efficiency($\eta$) |
| Water (Trial-1) | 30 | 49.4 | 4.18 | 0.711 | 57.65 | 5 | 52 | 600 | 211.2 | 0.272 |
| Water (Trial-2) | 30 | 67.6 | 4.18 | 0.711 | 111.74 | 11 | 3 | 600 | 397.8 | 0.280 |
| Water (Trial-3) | 30 | 83.8 | 4.18 | 0.711 | 159.89 | 15 | 37 | 600 | 562.2 | 0.284 |
| Water (Trial-4) | 30 | 97.1 | 4.18 | 0.711 | 199.41 | 19 | 19 | 600 | 695.4 | 0.286 |
| Average Efficiency | 0.281 $\approx 28$% |
The average efficiency obtained from the experiments is 28%. To find the optimal time required to boil the eggs perfectly, I took 3 eggs weighing 0.161 kg along with 0.721 kg of water and measured the initial temperature of the water and eggs (assuming both were at the same temperature since they were placed in the same container).
- Initial temperature 27.3 deg
- Final temperature 100 deg
- Specific heat capacity of water($C_{water}$) – 4.18 $KJ/kg^{o}C$
- Specific heat capacity of egg ($C_{egg}$) – 3.18 $KJ/kg^{o}C$
Using the below equation, the heat required($Q$) calculated as follows:
$$Q = m_{water}c_{water}(\Delta T)_{water} + m_{egg}c_{egg}(\Delta T)_{egg}$$
The amount of heat required to boil the water
$$\Delta U_{water} = 0.721 * 4.18 * (100 – 27.3) = 219.101 KJ$$
The amount of heat required to boil the eggs
$$\Delta U_{egg}= 0.161 * 3.18* (100 – 27.3) = 37.22 KJ$$
Total heat required is $Q = \Delta U_{water} + \Delta U_{egg}$
$$Q = 219.101 + 37.22 = 256.32 KJ$$
The amount of heat need to supplied by the induction stove
$$Q_{induction} = \frac{Q}{\eta}$$
$$Q_{Induction} = \frac{Q}{0.28}$$
$$Q_{Induction} = 915.4 KJ$$
With 600W power supply the time it take to hard boil the eggs
$$Time = \frac{Q_{Induction}}{P_{in}}$$
$$Time = \frac{915.4*10^{3}}{600}$$
So, the time required to boil 3 eggs with a total mass of 0.161 kg using 0.721 kg of water is 25.4 minutes
To put my calculation to the test, I used the same quantity of water and eggs and set the induction timer to 26 minutes at 600 W. After 26 minutes, I peeled and cut the eggs. As predicted by the calculation, the yolk was perfectly cooked with a slight orange tone (Reference image of boiled eggs with summary shown below).